Node Architecture & Trust Model
In the CENTAURON Network, each institution operates a Node — its sovereign entry point into a secure, peer-to-peer ecosystem for AI development in digital pathology. A Node defines the institution’s computational and data boundary, ensuring full control, regulatory compliance and autonomous participation.
Institutional Autonomy
A Node stores whole-slide images, metadata and ground truth locally. Data never leaves the institutional perimeter unless explicitly permitted. AI models come to the data and are executed on the Node; only evaluation metrics are returned. This preserves privacy, data ownership and diagnostic expertise.
Peer-to-Peer Collaboration
Nodes connect directly to each other — not through a central server. Participation is open to qualified medical and research institutions. Governance and trust are enforced cryptographically rather than via a platform operator, enabling scalable, transparent and institution-controlled collaboration.
Identity-Verified Participation
The network follows an open-membership but identity-verified model. Institutions authenticate via mutually trusted certificate authorities (CAs). CAs confirm institutional identity only and never gain access to medical data or influence collaborations, ensuring decentralized trust anchoring.
Hubs as Service-Nodes & Access Points
Hubs are full Nodes that optionally provide hosting and access services for institutions that do not operate their own infrastructure (e.g., smaller hospitals or labs). Beyond secure hosting, Hubs also simplify access for AI developers:
- Developers can discover datasets and Challenges across multiple independent institutions through a single interface and login
- A Hub routes AI submissions to participating data-owning Nodes for secure local execution
- Ground truth never leaves the data-owning institution; the Hub receives only aggregated metrics
- Hubs do not access protected data, do not govern participation and do not form a central authority
- Multiple independent Hubs may exist, preserving decentralization and preventing gatekeeping
- This ensures operational efficiency for multi-institutional AI development while maintaining full data sovereignty and * architectural decentralization.
Secure Local Execution
AI submissions are executed inside isolated containers on the respective data-owning Node. Mutual TLS secures Node-to-Node communication. Smart-contract logic verifies permissions before model execution, ensuring verifiable policy compliance and preventing unauthorized access.
Result
The Node architecture provides a decentralized, trust-verifiable foundation for collaborative medical AI. Institutions retain full control over their data and diagnostic value, join the network freely, and participate in global model development without exposing slides or relinquishing authority.
TL;DR
A CENTAURON Node is your institution’s secure gateway to global AI collaboration — data stays local, identity is verified, and only metrics leave. A Hub is a full Node that can host infrastructure and offer unified access for AI developers across many data providers — without gaining access to patient data or central control.
Components
The following schematic shows the architecture of a single node including the data owner and AI developer as share holders.
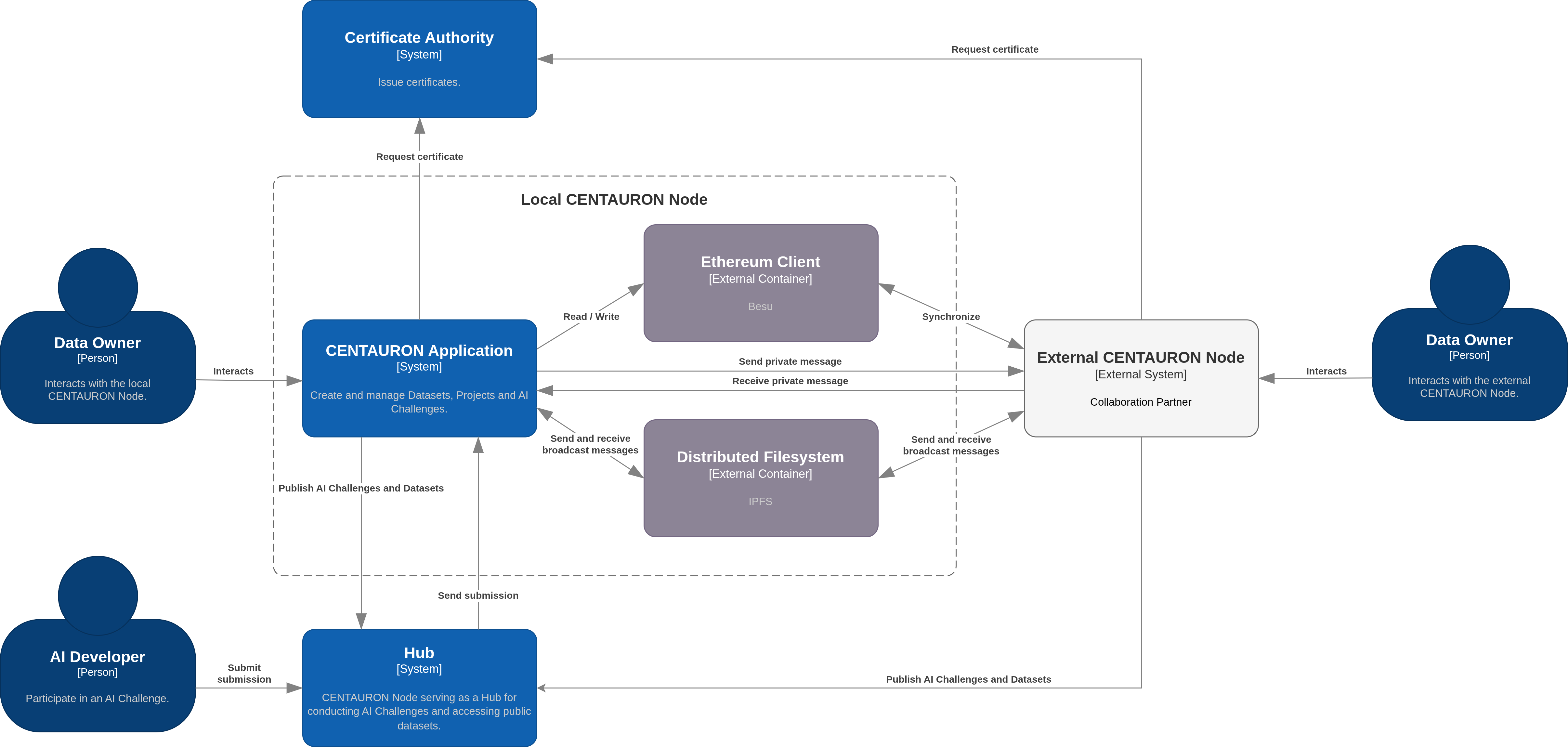
The following components are used:
- Besu: Ethereum blockchain node.
- IPFS: distributed filesystem for sending broadcasts to all Centauron nodes.
- Keycloak: Authentication and authorization on the local Centauron node.
- aria2: Download manager.
- Traefik: Reverse proxy.
- iipsrv: Whole Slide Image streaming.
- PostgreSQL: Database.
- redis: Cache.
- nginx: Reverse proxy.